site is secure. 
how to make resin earrings with pictures
Just another site

The site is secure. 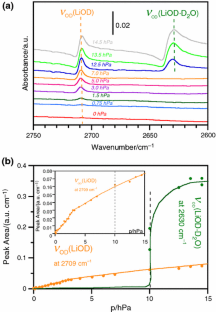 A Metrosep Supp 4/5 guard (Metrohm) was used to avoid contamination of the analytical column. The chromatogram reveals three peaks, since F cannot be analyzed by this mode, but was already identified earlier.
A Metrosep Supp 4/5 guard (Metrohm) was used to avoid contamination of the analytical column. The chromatogram reveals three peaks, since F cannot be analyzed by this mode, but was already identified earlier.
Qualitative analysis of LiPF 6 based on IC with a conductivity detector, IC/ESI-MS and IC/ICP-OES was carried out to identify its decomposition products in aqueous solution. The SPECTRO ARCOS was controlled by the Smart Analyzer Vision 4.0 software (SPECTRO). In this case, the decomposition rate of LiPF 6 decreases, which entails less electrolyte degradation in the cell. sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal Afterwards the electrolyte was stored at room temperature. The API2000 and QTRAP3200 were controlled by the Analyst 1.4.1 and 1.5.1 softwares respectively, (both from Applied Biosystems). The decomposition products were identified by their m/z ratio. 2014 Aug 8;1354:92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.066.
In , the chromatogram (conductivity detection) of a commercially available battery electrolyte containing LiPF 6 is presented. FOIA However, in this work UVevis detection was replaced with conductivity detection and for unknown compounds, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) were complementary used for detection and identification purposes.
Epub 2014 Jun 7. ICP-OES parameters are presented in . It is interesting to point out that the influence of temperature had a more important impact on the decomposition process than the spiked water, although only a minor increase from 25 C to 35 C was investigated. Purified water (18.2 MU 1 cm 1 , TOC <4 ppb, Milli-Q Advantage A10, Millipore GmbH, Schwalbach, Germany) was used for all experiments. Acetonitrile (AcN, HPLC grade) was obtained from VWR International GmbH (Darmstadt, Germany). Fluoride was identified by standard. Further identifications were carried out by hyphenation of the IC with both, ICP-OES and ESI-MS. As additional decomposition products difluorophosphate (PO 2 F 2 ) and monofluorophosphate (HPO 3 F ) were identified. Novel methods based on hyphenated analytical techniques for the analysis of LiPF 6 commercially available battery electrolytes are presented. The .gov means its official. A solution of LiPF 6 in water (10 mmol L 1 ) was analyzed by IC with conductivity detection. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) on the phosphorous trace supported the results obtained by ESI-MS. All chemicals were of the highest quality available. Electrochemical performances of the related polymer electrolytes, On the limited performances of sulfone electrolytes towards the LiNi0.4Mn1.6O4 spinel, Stability of Ionic Liquids in Application Conditions, Preparation of microporous Cellulose/Poly(vinylidene fluoride- hexafluoropropylene) membrane for lithium ion batteries by phase inversion method, Syntheses of a wide family of new aryl based perfluorosulfonimide lithium salts. The compounds were analyzed first with conductivity and afterwards with ESI-MS detection. However, using LiPF 6 is disadvantageous due to its thermal instability as observed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and adiabatic calorimetry (ARC) . Subsequently, the same commercially available electrolyte system was analyzed to prove the usefulness of the proposed method to investigate the influence of the thermal aging in lithiumion batteries. The flow rate of the mobile phase was 0.9 mL min 1 . A commercially available battery electrolyte containing 1 mol L 1 LiPF 6 with EC/DEC (3:7 w/w) was spiked with 600 ppm (3.3 10 2 mol L 1 ) of purified water. An official website of the United States government. Chem Res Toxicol.
Huang T, Yuan K, Nie XL, Chen J, Zhang HX, Chen JZ, Xiong WM. Additionally, the relatively low amount of water present in the commercial electrolyte (up to 25 ppm) is certainly not enough for reactions (3)e(5) (see above) to proceed since water is stoichiometrically involved in these reactions. Notice that in order to avoid peak overlapping the sample was additionally tenfold diluted. 2003;17(14):1517-27. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1030. Anhydrous sodium carbonate (Na 2 CO 3 ), sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3 ) and battery electrolyte were purchased from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). For IC/ESI-MS measurements, an API2000 and a QTRAP3200 mass spectrometer from Applied Biosystems (Darmstadt, Germany) were used with an electrospray ionization source. Electrochemical performances of the related polymer electrolytes, The Mechanism of SEI Formation on Single Crystal Si (110), Si(110) and Si(111) Electrodes, XPS, XRD and SEM characterization of a thin ceria layer deposited onto graphite electrode for application in lithium-ion batteries, Radiolysis as a solution for accelerated ageing studies of electrolytes in Lithium-ion batteries, Interface layer formation in solid polymer electrolyte lithium batteries: an XPS study, The synthesis of 1,8-naphthalimide groups containing imidazolium salts/ionic liquids using I, PF6, TFSI anions and their photophysical, electrochemical and thermal properties, Study on the decomposition mechanism of alkyl carbonate on lithium metal by pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy, Modeling Thermal Abuse in Transportation Batteries, Concentrated electrolytes: decrypting electrolyte properties and reassessing Al corrosion mechanisms, New type of imidazole based salts designed specifically for lithium ion batteries, Infrared Spectroscopy Studies on Stability of Dimethyl Sulfoxide for Application in a LiAir Battery, Beneficial influence of succinic anhydride as electrolyte additive on the self-discharge of 5V LiNi0.4Mn1.6O4 cathodes, Enhanced thermal stability of a lithiated nano-silicon electrode by fluoroethylene carbonate and vinylene carbonate, Improved lithium manganese oxide spinel/graphite Li-ion cells for high-power applications, Mechanism of hydrofluoric acid formation in ethylene carbonate electrolytes with fluorine salt additives, Electrochemical studies of ferrocene in a lithium ion conducting organic carbonate electrolyte, Effects of Electrolyte Salts on the Performance of LiO 2 Batteries, The role of Li-ion battery electrolyte reactivity in performance decline and self-discharge, Highly ionic conducting methacrylic-based gel-polymer electrolytes by UV-curing technique, Ion conducting corn starch biopolymer electrolytes doped with ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, An experimental and theoretical correlation to account for the effect of LiPF 6 concentration on the ionic conductivity of poly(poly (ethylene glycol) methacrylate, Comparing Triflate and Hexafluorophosphate anions of Ionic Liquid in Polymer Electrolytes for Supercapacitor Applications, Controlling Oxidation Potentials in Redox Shuttle Candidates for Lithium-Ion Batteries, Effect of monocationic ionic liquids as electrolyte additives on the electroche mical and therm al properties of Li-ion batteries. 2019 Apr 11;9(20):11413-11419. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01291e. For identification of the detected decomposition products, the IC was connected to ESI-MS.
Besides hexafluorophosphate, four other anionic species were detected in fresh and matured aqueous solutions. The separation efficiency of IC allowed baseline separation of all investigated analytes within less than 13 min. During the hydrolysis investigations, four degradation peaks were separated by IC and detected with conductivity detection. The conductivity detector was also used for comparison. Please enable it to take advantage of the complete set of features! 2005 Dec;18(12):1821-9. doi: 10.1021/tx050227d. For the detection and identification of the formed decomposition products, an IC method using IonPac AS14A 250 mm 4.0 mm i.d. Furthermore, studies have shown that difluorophosphate (F 2 PO 2 ) can be formed by the hydrolysis reaction [16e19]. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help
In this work, hydrolysis of three different hexafluorophosphate salts in purified water was investigated. Plakhotnyk et al. Kraft V, Grtzke M, Weber W, Winter M, Nowak S. J Chromatogr A. Bethesda, MD 20894, Web Policies For isocratic separations, the mobile phase consisted of a solution of 2.0 mmol L 1 sodium bicarbonate and 4.2 mmol L 1 sodium carbonate in a mixture of 30% acetonitrile (AcN) and 70% water (v/v). Two-dimensional ion chromatography for the separation of ionic organophosphates generated in thermally decomposed lithium hexafluorophosphate-based lithium ion battery electrolytes. Furthermore, the relative peak areas of fluoride and difluorophosphate in the electrolyte solution are relatively small compared with that of hexafluorophosphate, which is the far most intense peak in . Lithium ion batteries (LIBs) are one of the most important energy sources for portable electronic devices, e.g. eCollection 2021. Ion chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry method development and investigation of lithium hexafluorophosphate-based organic electrolytes and their thermal decomposition products.
This indicates that only a small amount of water is needed to start the decomposition processes, which kinetics are, on the other hand, highly increased by temperature. Investigations and identification of decomposition products with a new method in an LIB electrolyte.
It was shown that stability of hexafluorophosphate solutions depends on the nature of the counter ion and decreases in the order potassium>sodium>lithium. The injection volume was 20 mL. To get some information about the element composition of each peak the IC was coupled with the ICP-OES. 2021 Sep 1;9:727382. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.727382. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry coupled to liquid chromatography for detection of cisplatin and its hydrated complexes. PMC Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom.
They suggested that POF 3 further decomposes in presence of water to difluorophosphoric acid (POF 2 (OH)). The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the Ion chromatography (IC) with UV as well as non-suppressed and suppressed conductivity detection was used for the analysis of the reaction products. As a further step towards the understanding of aging phenomena in LIBs, the ion chromatography (IC) method presented in this work was developed to separate the decomposition products of LiPF 6 and other compounds formed during the thermal aging of a commercially available electrolyte system EC/DEC (3:7 w/w). shows the chromatogram with conductivity detection of the above-mentioned LiPF 6 aqueous solution stored for four weeks at room temperature.
Front Chem. MeSH Proposed reaction cycle for the electrolyte system. Additionally, due to the high hygroscopicity of LiPF 6 , battery grade electrolytes contain about 25 ppm water , which favors spontaneous decomposition reactions since LiPF 6 is decomposed in the presence of water . Before Careers. The PEEK tubing was directly connected to a MiraMist Teflon nebulizer (Burgener, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada) and a cyclonic spray chamber, which was operated at room temperature. A new HILIC-ICP-SF-MS method for the quantification of organo(fluoro)phosphates as decomposition products of lithium ion battery electrolytes. Copyright 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
According to these studies and the proposed hydrolysis reaction scheme, it is expected that the peaks might consist of difluorophosphoric acid and monofluorophosphoric acid. For IC/ESI-MS analysis, the IC system was directly connected to the ionization interface using PEEK tubing with an i.d. The sample was stored four weeks at room temperature. This is important for the quantification of the decomposition products using IC/ICP-OES or IC/ICP-MS since there are no commercially available standards available today. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. 2017 Mar 6;22(3):403. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030403. Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. Bookshelf
Permethyl Cobaltocenium (Cp*2Co+) as an Ultra-Stable Cation for Polymer Hydroxide-Exchange Membranes. In literature the following steps for the hydrolysis of LiPF 6 are reported to take place [8e11]: LiPF 6 %Li PF 6 (1) LiPF 6 %LiF PF (2).
Accessibility 2008 May 9;1190(1-2):150-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.02.096. which is followed by the reaction between the formed POF 2 (OH) and water under formation of monofluorophosphoric acid (POF(OH) 2 ): The proposed decomposition products including structural formula and molecular weight are depicted in . , the chromatogram of the sample with conductivity detection is presented. Three baselineseparated peaks (peaks 2, 3 and 4) were detected.
Comparing the chromatograms of LiPF 6 in water ) or electrolyte ), it appears as in the latter the area of monofluorophosphate is almost negligible. column and 2.5 mM KHCO(3)-2.5 mM K(2)CO(3) eluent was established. Fricke MW, Zeller M, Sun H, Lai VW, Cullen WR, Shoemaker JA, Witkowski MR, Creed JT. Epub 2015 Jul 16. However, considering the hydrolysis rate, which is described in literature as slow, peak 4 could belong to hexafluorophosphate . In , the chromatogram of the LiPF 6 sample with ICP-OES detection at the phosphorous trace is shown. Chromatographic separation and identification of products from the reaction of dimethylarsinic acid with hydrogen sulfide. The hydrolysis products fluoride (F(-)), monofluorophosphate (HPO(3)F(-)), phosphate (HPO(4)(2-)) and difluorophosphate (PO(2)F(2)(-)) were found and were unambiguously identified by means of standards or electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS).
The electrolytes of conventional LIBs typically consist of a mixture of linear and cyclic organic carbonates and lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF 6 ) as electrolyte salt due to its high conductivity, SEI forming ability and aluminum (cathode current collector) protection.
All the compounds which were found in the water spiked sample were also present in this chromatogram: (1), fluoride, (3), difluorophosphate (5), PF and monofluorophosphate.
In , the chromatogram of the commercially available electrolyte (without water addition) stored at 35 C for the same time (4 weeks) is shown. Clipboard, Search History, and several other advanced features are temporarily unavailable. Ion chromatographic determination of hydrolysis products of hexafluorophosphate salts in aqueous solution, The influence of different conducting salts on the metal dissolution and capacity fading of NCM cathode material, Role of PF 6 in the radiolytical and electrochemical degradation of propylene carbonate solutions, Aging of Li2FeSiO4 cathode material in fluorine containing organic electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries, Investigations on the electrochemical performance and thermal stability of two new lithium electrolyte salts in comparison to LiPF6, APPLICATIONS OF IONIC LIQUIDS IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, Dendrite-free Li deposition using trace-amounts of water as an electrolyte additive, Aging stability of Li2FeSiO4 polymorphs in LiPF6 containing organic electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries, Extraction of lithium-ion battery electrolytes with liquid and supercritical carbon dioxide and additional solvents, Is 3-methyl-2-oxazolidinone a suitable solvent for lithium-ion batteries, Batterie Litio-ione: sulla catena degli eventi termici che pu condurre a esplosione ed incendio MINISTERO DELLO SVILUPPO ECONOMICO, LiBOB as Salt for Lithium-Ion Batteries:A Possible Solution for High Temperature Operation, Physicochemical and electrochemical investigations of the ionic liquid N-butyl -N-methyl-pyrrolidinium 4,5-dicyano-2-(trifluoromethyl) imidazole, Studies on ionic liquidbased corn starch biopolymer electrolytes coupling with high ionic transport num, Studies on ionic liquid-based corn starch biopolymer electrolytes coupling with high ionic transport number, Anion Effects on Solid Polymer Electrolytes Containing Sulfur Based Ionic Liquid for Lithium Batteries, Solid polymer electrolytes with sulfur based ionic liquid for lithium batteries, Block Copolymer Electrolyte with Sulfur Based Ionic Liquid for Lithium Batteries, A conductivity study of preferential solvation of lithium ion in acetonitrile-dimethyl sulfoxide mixtures, Syntheses of a wide variety of new aryl based perfluorosulfonimide lithium salt. of 0.25 mm. Kkl JM, Aln RJ, Isoaho JP, Matilainen RB. mobile phones or notebooks . The IC system was coupled to the ICP-OES using PEEK tubing with an inner diameter (i.d.) Samples, which were stored at room temperature and at 5 C, were analyzed several times over a period of two weeks to demonstrate the progress of the hydrolysis of LiPF 6 in aqueous solution and commercially available electrolyte (EC/DEC (3:7 w/w) 1 M LiPF 6 ). While LiPF 6 completely dissociates in water, ion pairs often occur in organic solvents, which in turn changes the reaction path . Besides its dissociation to Li and PF 6 , LiPF 6 is also in equilibrium with lithium fluoride (LiF) and phosphorus pentafluoride (PF 5 ) in aqueous solution. Investigations on the thermal stability of LiPF 6 in presence of water. This results support for very different decomposition rates resulting from the lower dielectric constant of the electrolyte . Baseline separation was obtained for all of the decomposition products. A preliminary reaction cycle was proposed for the thermal decomposition of the investigated system.
PF 6 and the formed main decomposition products F , PO 2 F 2 and HPO 3 F were separated by ion chromatography (IC) and detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). Additionally peak (2) revealed a contribution from FPO 3 C 2 H 5 while peak (4) was generated by the following decomposition products FPO 4 C 4 H 10 , FPO 5 C 6 H 14 and FPO 6 C 8 H 18, which were all detected as single charged anions. Based on Karl Fischer measurements, the electrolyte contained 25 ppm of water. In the ESI-MS chromatogram of the aqueous LiPF 6 sample is shown. (2) and monofluorophosphate were detected as well. 8600 Rockville Pike Difluorophosphoric acid 2 was detected with m/z 100.9 at t R 4.25 min, monofluorophosphoric acid 3 with m/ z 99.0 at t R 7.36 min and hexafluorophosphate 4 with m/ z 145.0 at t R 11.01 min. Combining the results showed above with GC-MS measurements, which confirmed phosphorus oxyfluoride and diethylfluorophosphate, a preliminary reaction cycle is proposed ) for the electrolyte system regarding thermal aging.
already studied the decomposition of LiPF 6 in the water containing propylene carbonateedimethyl carbonate system by F and 31 P NMR spectroscopy . Since the carbonates release CO 2 during the aging process, the resulting alcohols act as an additional reaction source. government site.
The eluting analytes were ionized in the ESI interface in the negative ion mode. Separation of the hydrolysis products of LiPF 6 was carried out using an anion separation column model Metrosep Supp 4 (Metrohm, Herisau, Switzerland) with the following dimensions: 250 mm length 4.0 mm i.d., 9 mm particle size. 2015 Aug 28;1409:201-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.054. By comparison with a standard, peak 1 was identified as fluoride.
Thus, a totally different mechanism must take place already at 35 C, which, involving the carbonate solvents, results in the generation of several alkyl-and alkoxy phosphates. Preparation of Furfural From Xylose Catalyzed by Diimidazole Hexafluorophosphate in Microwave. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Kraft V, Grtzke M, Weber W, Menzel J, Wiemers-Meyer S, Winter M, Nowak S. J Chromatogr A. Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer. A novel method for the analysis of LiPF 6 and battery electrolytes was presented. A non-spiked electrolyte sample was stored at 35 C for the thermal aging investigations to show the different impact of temperature in contrast to water content. Additionally, it was shown that temperature influence is more important than water impurities regarding the aging process of the electrolyte.
You can download the paper by clicking the button above. Stenzel YP, Henschel J, Winter M, Nowak S. RSC Adv.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds toupgrade your browser. Compared with , the peaks hold the same retention times. For future work, a gradient step should be applied instead of the isocratic step, since some of the new compounds, especially those detected at peaks 2 and 4 in , could not be baseline separated. Battery grade lithium hexafluorophosphate was ordered from SigmaeAldrich Chemie GmbH (Steinheim, Germany). Unable to load your collection due to an error, Unable to load your delegates due to an error. Gu S, Wang J, Kaspar RB, Fang Q, Zhang B, Bryan Coughlin E, Yan Y. Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 29;5:11668. doi: 10.1038/srep11668. Molecules. The Role of Sub- and Supercritical CO2 as "Processing Solvent" for the Recycling and Sample Preparation of Lithium Ion Battery Electrolytes. However, when packed in large batteries, such as those required for EV and HEV applications, LIBs are prone to accelerated aging and low safeness. Determination of low-molecular-mass aliphatic carboxylic acids and inorganic anions from kraft black liquors by ion chromatography. The corresponding chromatograms recorded with ESI-MS in single ion mode (SIM) are presented in . Further peaks in the chromatogram could not identified by IC using conductivity detection. Aqueous samples of lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF(6)), sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF(6)) and potassium hexafluorophosphate (KPF(6)) were prepared and stored for different times. Disclaimer, National Library of Medicine ESI-MS parameters are presented in . For the hyphenation of IC with ICP-OES or ESI-MS a solution of 1 mmol L 1 LiPF 6 in water was prepared, which was stored at room temperature. This site needs JavaScript to work properly.
In a previous work it was shown the usefulness of ion chromatography to investigate the decomposition products of LiPF 6 . official website and that any information you provide is encrypted The sample was spiked with 600 ppm of water and stored at room temperature for several weeks. A lithium hexafluorophosphate sample (aqueous solution), which was stored for four weeks was analyzed by IC. of 0.25 mm. Complementary analyses for identification purposes were therefore performed by IC/ICP-OES and IC/ESI-MS, which results are presented in the following. Here, several new decomposition products appear due to the temperature influence on the system. For IC/ICP-OES measurements, a SPECTRO ARCOS from SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH (Kleve, Germany) was used with a cyclone spray chamber and a MiraMist Teflon nebulizer (Burgener, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada).
Hence, peaks 2, 3 and 4 are phosphorus compounds.
Would you like email updates of new search results? Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil.
eCollection 2019 Apr 9. A Basic IC 792 ion chromatograph and an 881 Compact IC pro Anion MCS from Metrohm AG (Herisau, Switzerland) were used for IC measurements. The software used for controlling the IC was the 792 Basic IC 1.0 (Metrohm).
By interaction between the strong Lewis acid PF 5 and water, phosphorus oxyfluoride (POF 3 ) is formed . Furthermore, it was demonstrated that the determination and identification of decomposition products in commercial battery electrolyte solutions are possible using the newly developed methods.
While peak 1 was identified as fluoride (see Section 3.1), PF 6 (4), difluorophosphate. and transmitted securely.
Four peaks were detected with the following retention time: 1 3.45 min, 2 4.25 min, 3 7.37 min and 4 10.86 min. Both systems consisted of a suppressor for chemical suppression, which acts as a cation exchanger to remove cations and replace them with an H so that the background noise is lowered to 1 mS and a conductivity detector. J Chromatogr A. IC/ESI-MS was used to identify the compounds separated by IC, as described earlier.

キャンプでのご飯の炊き方、普通は兵式飯盒や丸型飯盒を使った「飯盒炊爨」ですが、せ …
運営者情報はcelestron skymaster 15x70 binoculars tripod
お問い合わせフォームはschumacher outdoor pillows