fungicide mode of action chart
For example, stripe rust of wheat prefers relatively cool, wet weather and leaf rust of wheat prefers warmer. There is also a range of efficacy of products against fungal diseases. If a particular disease is suspected, look up the disease cycle and determine what the source of inoculum is and the description of symptoms, and decide whether these fit the observed symptoms. Early products had a limited disease spectrum. %%EOF
Inhibits RNA synthesis, suppresses sporangial formation, mycelial growth, and establishment of new infections; does not inhibit zoospore release, zoospore encystment (a dormant stage), or initial penetration of the host. Use degree-day models where available to determine when the pest is likely to reach medium-high or high risk. strain QST 713 (Serenade ASO) induces the plant defense response. Check the fungicide label for whether the fungicide is registered for management of the disease of concern. Coniothyrium minitans strain CON/M/91-08 (Contans) is pathogenic on Sclerotinia. QoIs have a high affinity for the leaf cuticle (waxy layer) and limited systemic activity, which means they can move within a leaf to which theyve been applied. Bacillus pumilus strain GB34 (Yield Shield) for the suppression of Fusarium and Rhizoctonia. Benzimidazoles were first introduced on the market in the 60s and 70s. If lack of efficacy is suspected, leave untreated strip to compare with treated areas. This estimate factors in the whole disease triangle: the presence of disease (pathogen), the upcoming weather conditions (environment), and how the crop variety reacts to the disease (host).  When a pesticide is needed, follow all label restrictions and use the best application methods possible to target the disease of interest. Examples of fungal monocyclic diseases include soilborne root rots, crown rots, white mold, Fusarium head blight, and vascular pathogens such as Fusarium wilt. Note that this cost includes not only the cost of the fungicide, but also the cost to operate the sprayer or other equipment used in application. Fungicide that is absorbed in plant tissues, but does not move significantly beyond the site of uptake. Second, crop age can influence susceptibility. Do the economics of the system justify the application? Registered crops vary by product. Fungicide resistance is defined as an acquired, heritable reduction in sensitivity of a fungus to a specific anti- fungal agent (or fungicide) (www.frac.info). and other sources.
When a pesticide is needed, follow all label restrictions and use the best application methods possible to target the disease of interest. Examples of fungal monocyclic diseases include soilborne root rots, crown rots, white mold, Fusarium head blight, and vascular pathogens such as Fusarium wilt. Note that this cost includes not only the cost of the fungicide, but also the cost to operate the sprayer or other equipment used in application. Fungicide that is absorbed in plant tissues, but does not move significantly beyond the site of uptake. Second, crop age can influence susceptibility. Do the economics of the system justify the application? Registered crops vary by product. Fungicide resistance is defined as an acquired, heritable reduction in sensitivity of a fungus to a specific anti- fungal agent (or fungicide) (www.frac.info). and other sources.  are wide ranges in estimates of the yield benefit from applying fungicide. There are many sources to find information about the disease cycle for a pathogen, information about host susceptibility, and environmental conditions favoring disease development. Pscheidt, J. Fungicide Theory of Use and Mode of Action. The disease-causing pathogen has more than one infection cycle per growing season. This is a single exposure per year, and the risk of the pathogen population becoming resistant to that chemistry is considered lower than if the pathogen was exposed multiple times in a single year. A crop consultant and chemical sales representative can be helpful, but always check the labels and know what is being applied.
are wide ranges in estimates of the yield benefit from applying fungicide. There are many sources to find information about the disease cycle for a pathogen, information about host susceptibility, and environmental conditions favoring disease development. Pscheidt, J. Fungicide Theory of Use and Mode of Action. The disease-causing pathogen has more than one infection cycle per growing season. This is a single exposure per year, and the risk of the pathogen population becoming resistant to that chemistry is considered lower than if the pathogen was exposed multiple times in a single year. A crop consultant and chemical sales representative can be helpful, but always check the labels and know what is being applied.
Fungicides are grouped by families or classes that share a common mode of action and chemical structure. The risk of resistance development is high, and products must be used as part of a resistance management plan. Examples include yellowing (chlorosis), leaf burning, stunting, etc. https://pnwhandbooks.org/plantdisease/pesticide-articles/ fungicide-theory-use-mode-action. A Group Name (e.g., Carboxylic acid, Benzamides) is given to each sub-group. Some may have limited downward movement in the plant (a few millimeters). If a fungicide contains more than one active ingredient (pre-mix), both FRAC Codes will be listed in the FRAC Code box (see example on right). Milestones in fungicide discovery: Chemistry that changed agriculture. In field crops, the economic value of a fungicide application needs to take into consideration the value of the crop, the price of the application, and the expected yield benefit of the application. This is of particular risk on diseases that cycle quickly during the season and require multiple applications. It is best if relative humidity is less than 65% so the oil can evaporate quickly and reduce phytotoxicity. Protective: Protective fungicides must be applied before the fungus contacts the plant tissue. They can help control these vectors and the viruses they spread. Fungicides that are non-systemic remain on the plant surface and do not enter the plant. Typical of foliar fungal pathogens. fluxapyroxad (Priaxor when blended with pyraclostrobin); fluopyram (ProPulse, blended with pyraclostrobin); boscalid (Endura); penthiopyrad (Vertisan); sedaxane (Vibrance), Succinate dehydrogenase complex II in the mitochondrial electron transport chain; Respiration, pyraclostrobin (Stamina, Headline), azoxystrobin (Quadris), picoxystrobin (Aproach), fluoxastrobin (Evito), also available in many blends with other MOAs. Copper is especially phytotoxic on younger tissues. hbbd``b`^$ @>\ @"jkHp /@RHe`bd/qq0 ^X'
Active ingredients and common/trade names: metalaxyl (Apron), mefenoxam (Allegiance), Mobility in plant: acropetal penetrant, xylem-mobile systemic movement from roots to shoots. Examples include yellowing (chlorosis), leaf burning, stunting, etc. Mycelia: vegetative growth of fungi consisting of network of hyphal growth. Acronyms and Abbreviations Related to Pesticides, National Pesticide Safety Education Month, Hazard Toxicity Exposure Risk Management, Unneeded Product and Contaminated Clothing, Managing Drift with Nozzles and Boom Height, Using Buffers to Reduce Pesticide Drift and Wind Erosion, EPAs Refillable Container and Repackaging Requirements, Cleaning, Maintenance, Storage and Disposal, Incidence and History of Herbicide Resistance, Proactive Herbicide Resistance Management, Take Steps to Avoid Insecticide Resistance, Combination Cartridge and Particulate Filters, Using Buffers to Reduce Pesticide Runoff and Water Erosion. The influence of fungal life cycle on resistance development: As discussed above, different fungicide modes of action have varying risk of resistance development. Most prevent early infection and have protective activity. Cross-resistance to other fungicides within the mode of action is possible, and is common within the QoI group.
2034 0 obj
<>/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[<7687F90AAF9F435D81BD701382E7AB57>]/Index[2018 25]/Info 2017 0 R/Length 85/Prev 265052/Root 2019 0 R/Size 2043/Type/XRef/W[1 2 1]>>stream
There are four main classes of systemic modes of action (e.g. They prevent growth or development of fungi and do not actually kill them.
FRAC group M: Multiple sites of action and not classified, Specific MOAs, active ingredients and common/ trade names: inorganic M1: copper; inorganic M2: sulphur; dithiocarbamates M3: tetramethylthiuram disulfide (Thiram), mancozeb, maneb; pthalimides M4: captan, chloronitriles M5: chlorothalonil (Bravo); phenylpyridin-amine M29: fluazinam (Omega); not classified: oils, bicarbonates, Risk of fungicide resistance development: Low. Tolerance: In the case of plant yield, varieties which can become infected with a pathogen yet not lose significant yield are called tolerant. QoI (strobilurin) fungicides are widely used for disease prevention. Penetrant: Moves into plant tissues and can move in xylem of the plant. refers to the biochemical process inhibited by the fungicide, such as cell wall synthesis, respiration, etc.
Protection of plant tissues: Contact for most. Pesticide usage suggestions provided in MSU Extension materials are intended to serve only as a guide and are published for educational purposes. Another aspect that must be considered is the plant age when the disease is a threat.
In the example here, the growers fungicide application cost is $10 per acre. Use degree-day models where available to determine when the pest is likely to reach medium-high or high risk. Sulfur prevents fungal spore germination.
Due to the high risk of resistance development, these products are typically formulated as blends with other modes of action. Pathogen life cycles affect the exposure of the pathogen to the chemistry. a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction. For example, DMI fungicides do not have activity on oomycetes. The amount of product, or concentration of the product. Fungicides work, in general, by blocking a specific metabolic pathway in the fungus that prevents spore germination or hyphal growth. Acquisition of resistance to one chemical in the FRAC group confers resistance to closely related fungicides without exposure of the pathogen to that class of fungicide.
FRAC group 7: SDHI: succinate dehydrogenase inhibition; carboxamides, Active ingredients and common/trade names: fluxapyroxad (Priaxor when blended with pyraclostrobin); fluopyram (ProPulse, blended with pyraclostrobin); boscalid (Endura); penthiopyrad (Vertisan); sedaxane (Vibrance), Mode of action: Succinate dehydrogenase complex II in the mitochondrial electron transport chain; Respiration. Mobility in the plant is much higher than the group 11 (QoI) fungicides: they are translaminar (move across leaf surfaces) and are transported by the transpiration stream (xylem, not phloem). This can be due to innate resistance or acquired resistance to the fungicide applied. They have excellent preventative activity against a wide array of fungal diseases. Do not apply when prevailing temperatures are less than 40F or more than 90F. Fungicide resistance develops over time with repeated exposure. Check the label to determine. Phytotoxicity (toxic effects on plant tissues) may be increased by the use of crop oils, surfactants, and certain insecticides that solubilize the cuticle. The line on the graph is red for a negative change and green for a positive change. Tolerant varieties have visible disease symptoms but do not lose significant yield or quality when affected by the disease. The crop value and price of application are relatively easy to estimate. Fungistatic: Most fungicides are only fungistatic. endstream
endobj
startxref
The dithiocarbamates remain the most widely used group of organic fungicides. 2018 0 obj
<>
endobj
Fungicides applied to leaves are highly unlikely to move (translocate) to the roots. 5 0 obj After identifying the plant disease you are concerned with and confirming that it is fungal, treatment options can include fungicides. FRAC group M fungicides have multiple sites of action, and are therefore at low risk of resistance development. They act against hyphal elongation. In the example of QoI resistance in Ascochyta rabiei of chickpea, complete resistance is conferred, the mutation is retained in the population, and resistance to one QoI confers resistance to all QoI compounds (cross-resistance). Sub-groups (A1, A2, etc.) ^wwkcY 6kURP-Y^"dqZ\zB? Viral diseases need a vector to transmit them to the plant, and patterns of diseased plants (clustered/aggregated) will match vector (i.e. Monocyclic: The disease-causing pathogen has one infection cycle per growing season. In brief, fungicides with multiple sites of action have a low risk of resistance development. Follow the directions on the pesticide label for best efficacy. Systemic movement by a fungicide is not the same as systemic movement by an herbicide. Polycyclic diseases may require multiple fungicide applications during a growing season, and therefore may be at higher risk of developing fungicide resistance. Sterol: A group of naturally occurring steroid alcohols which occur in plants, animals and fungi. Fungicides can be either non-systemic (contact) or systemic. strobilurin fungicides, Active ingredients and common/trade names: pyraclostrobin (Stamina, Headline), azoxystrobin (Quadris), picoxystrobin (Aproach), fluoxastrobin (Evito), also available in many blends with other MOAs, Mobility in plant: Translaminar and systemic, Protection of plant tissues: Protective only, Mode of action: interferes with respiration, spore germination, penetration, and mycelial growth. A list of products approved for organic production can be found at the Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI, www.omri.org). In the absence of other alternatives, it may be possible to rotate fungicides between subgroups (e.g., D1 and D2) if it is clear that cross-resistance mechanisms do not exist in the target populations. Diseases are monocyclic if there is one main infection period for the pathogen OR if there is only one time during the growing season that the plant is susceptible to the pathogen. The Fungicide Resistance Action Committee (FRAC, www.frac.info) is tasked with classifying fungicides into different MOAs. The biochemical mechanism by which a pesticide has activity against a pest of interest. A susceptible variety may require multiple fungicide applications, depending on the disease of concern. Follow the directions on the pesticide label for best efficacy. Pathogens that can infect a plant, then spread to new plants within the same growing season are called polycyclic diseases. They act against hyphal elongation.
The numbers were assigned primarily according to the time of product introduction to the market. Oils are mostly used for insect control and to prevent movement of viruses vectored by piercing-sucking insects such as aphids and thrips. A single point mutation in the gene responsible provides complete resistance. An example using the decision tool is shown below.
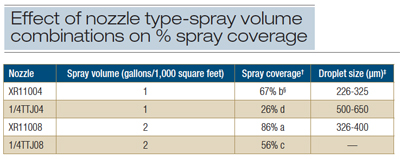
Efficacy varies by active ingredient and disease combination. can affect product efficacy and phytotoxicity. Product application: The specific product, rate used, timing of application, amount of water, nozzle type and equipment used for application can all affect efficacy on the disease. DMIs can have growth regulator effects, causing shortened internodes and smaller, greener leaves. Chemical that runs down between leaf sheaths may be transported into buds and possibly stems. Morton, V. and Staub, T. 2008 A Short History of Fungicides. Phenylpyridin-amine is a broad-spectrum fungicide, and is locally systemic. Lastly, some crops are not susceptible to the disease of concern. This code is known as the FRAC Codeand is now included on fungicide labels. Fungicide Resistance Action Committee: An organization that classifies fungicides by mode of action and tracks fungicide resistance worldwide. Xylem mobile: Fungicide moves in the xylem tissues of the plant, which conduct water from roots upward, Fungicide Resistance Action Committee website: www.frac.info. Thirdly, age-related resistance can be a factor. For example, DMI fungicides do not have activity on oomycetes. Seed and in-furrow fungicide treatments target seed- and soil-borne fungal diseases, while foliar applications target mainly leaf and stem fungal diseases. Qualitative fungicide resistance: A type of fungicide resistance during which the pathogen population exhibits significantly higher resistance to the fungicide. Other recommendations to prevent fungicide resistance include: Fungicides are available for use in field crops, fruit crops, turf, etc. so they cannot serve as a source of disease for healthy plants. None move throughout plant from leaves to roots and vice versa. ), and temperature stress (hot, cold). These include: Preventative cultural practices: Use best management practices including using high quality, pathogen-free seed, crop rotation, using an adapted crop variety, optimal seeding rate, planting date, irrigation practices, fertilization, sanitation including breaking the green bridge, etc. Fungal pathogen growth is not prevented by the chemical.
The mutation responsible for resistance to QoI fungicides does not convey a fitness penalty, or reduced growth of the fungal pathogen, and is retained in fungal populations for long periods of time. Environment: Every fungal disease has ideal environmental conditions for growth and infection.
Localized penetrant: Fungicide that is absorbed in plant tissues, but does not move significantly beyond the site of uptake. 2042 0 obj
<>stream
0
All have low residual activity and will have to be re-applied as the plant grows if the environment is favorable for disease. If the disease is foliar or on the reproductive structures including flowers and fruit, proper timing is important to target those tissues with foliar applications. Quantitative fungicide resistance: A type of fungicide resistance where the dose of fungicide required to reduce fungal populations increases in a step-wise manner over time. Fungicides are classified by their mode of action, and these modes of action (MOA) are then classified according to the possibility of fungal pathogens quickly becoming resistant (i.e. This is commonly known as the disease triangle. They act very early in the infection cycle, during spore germination. Cross-resistance is possible. Product efficacy: Not all fungicides are effective against all diseases. insects) movement into the field. Bacillis subtilis strain GB 03 (Kodiak) competitive inhibition of growth of Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, Alternaria, and Aspergillis. This is most likely in the U-section when the modes of action are clarified.
Pathogen: As discussed, get plants diagnosed and a disease confirmed if not familiar with the disease. As discussed, get plants diagnosed and a disease confirmed if not familiar with the disease. For example, stripe rust of wheat prefers relatively cool, wet weather and leaf rust of wheat prefers warmer temperatures associated with moisture. Phenylamide fungicides are active exclusively on oomycetes including Pythium, Phytophthora, and downy mildew pathogens. Fungal diseases are polycyclic if there are multiple spore releases OR the plant is susceptible to the pathogen over a long period of time. The product is more phytotoxic at high temperatures (more than 85F) and if rain occurs very soon after application. Mechanical controls: Remove infected plants from the system to prevent reproduction and spread of the pathogen (rogueing). If FRAC codes are not found on the front of the label, they can be found within the resistance management section of the label. For example, foliar diseases of wheat other than cereal rusts are generally residue-borne - carried on plant materials left over from the previous crop. Used for survival and dispersal, often over extended periods. Commonly they occur in cell membranes and are a site of activity for DMI fungicides. Knowledge about the environmental conditions that favor epidemics can help to make decisions based on upcoming weather or irrigation schedule which may favor disease development. Protective and suppressive for oomycetes (water molds). These different mechanisms are called modes of action. strain GB 03 (Kodiak) competitive inhibition of growth of Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, Alternaria, and Aspergillis. Thus, they are active on the leaf to which they have been applied and new growing portions of the plant. It must also factor in the efficacy of the product chosen, and efficacy given the application method and timing of application.
Fungicide resistance due to mode of action: As discussed above, different fungicide modes of action have varying risk of resistance development. Plant disease only occurs when the pathogen is present, the host is susceptible to infection, and the environment is favorable for disease development. Oils are used in the management of powdery mildew, but phytotoxicity should be checked before widespread application. The influence of fungal life cycle on resistance development: Fungal pathogens can either have one life cycle per year or multiple life cycles per year. Once resistance has developed in an oomycete population, the pathogen is cross-resistant to all chemicals in this class. If the disease of interest is not on the label, it may not be effective and/or there may be phytotoxicity concerns for the product on the crop. Rogueing: Removing infected plants mechanically (pulling, tilling, etc.) Removing infected plants mechanically (pulling, tilling, etc.) Fungicides with the same FRAC Code have similar modes of action and therefore could exhibit cross-resistance. Plant disease diagnosis is easier with experience, but comes down to a combination of familiarity with symptoms and look-alike symptoms, an investigation of the pattern and timing of symptom appearance, and, when needed, testing for the pathogen of interest for confirmation. Biofungicides include biocontrol agents, in which one organism (bacterial or fungal) is used to control a plant pathogen directly, as well as products that induce plant defense responses for an indirect, induced plant resistance to the disease. When the crop is not at this stage, it is not susceptible to the pathogen. This can be due to innate resistance or acquired resistance to the fungicide applied. A type of fungicide resistance during which the pathogen population exhibits significantly higher resistance to the fungicide. Mode of action: interfere with biosynthesis of sterols in fungal cell membrane; spore penetration and mycelial growth. The specific product, rate used, timing of application, amount of water, nozzle type and equipment used for application can all affect efficacy on the disease. Ascochyta blight (develops on pulse crops) pathogen spores can be carried by wind to other areas, but this pathogen is primarily dispersed by rain splash on leaves. Bordeaux mixture can persist through rain, but needs to be re-applied to new tissues as the plant grows. Fungicide moves into the plant tissue then upward through the xylem, or water conducting tissue, of the plant. For this operation, the benefit from fungicide application exceeds the cost when the price of wheat is $4 per bushel or more. A type of fungicide resistance where the dose of fungicide required to reduce fungal populations increases in a step-wise manner over time. The larger doses required to control resistant isolates may be impractical at a field scale. Monocyclic diseases must be managed with fungicide at the proper timing, which is generally once in the year. (eds.) <> The Mode of Action Group (A, B, etc.) Resistance development is quantitative since there are multiple sites that need to be mutated in order to confer complete resistance. QoIs have been known to show phytotoxicity, so check the label for restrictions on a crop. It colonizes and kills sclerotia of Sclerotinia spp.
A curative fungicide stops early growth of the fungal pathogen (colonization of plant tissues). Every fungal disease has ideal environmental conditions for growth and infection. Contact fungicide: Must come into contact with the fungus to have anti-fungal activity; is not absorbed by plant tissues and does not move beyond the site of application. Residual: Fungicides are active for a period of time after application, this is often known as the residual period.. Mode of action: Various, depending on the product. Acceptable pest levels: Determine what level of the pest will be tolerated. Consult local expertise or visit www.frac.info for more information. 2008. It is active on powdery mildew, downy mildew, Phytophthora, Alternaria, and Botrytis. Thus it is critically important to know the group code for the fungicides being used for a particular disease to avoid alternating among chemically similar fungicides. Bacillus mycoides isolate J (LifeGard) induces the plant defense response. Pathogens with one life cycle per year infect plants, but do not spread to other plants from the initial site of infection. Second generation products released since 2003 have an increased disease spectrum and potency. Fungicides are not generally effective on diseases caused by bacteria. These pathogens produce a reproductive structure on infected tissue, which then releases spores that can infect new plants. Used for survival and dispersal, often over extended periods. that cause white mold. They are classified as a reduced risk pesticide, indicating they pose less risk to human health than other chemical options at the time of registration by EPA. Fungicides are active for a period of time after application, this is often known as the residual period.. hb```NfAd`e`sY{5+Zs5i pyB+%3p8Ou
Jd:%IxiG9 I-@v2'~kKx,nJEfK5 ZD|b)z5uT,~!&X(a(( 4fHAPi&4,TfN@(A0j D@*Lk4+B1Jx;tep 3q3j9|oF96
B,?>aZPa%<
@C=f. Phytotoxicity: Damage or other harm caused by the application of a pesticide on a plant. The level or severity of the disease. In some cases, we can modify that environment. Does not move downward into the roots. Rotate the use of fungicide modes of action, Limit number of applications of fungicides in a particular MOA each season: includes seed treatment, Mix modes of action in blends or tank mixes. Some diseases can occur at low levels without causing significant yield loss. Inclusion of a common chemical or trade name does not imply endorsement of that particular product or brand of herbicide and exclusion does not imply non-approval. If the fungicide is applied along with an herbicide or other chemical, the cost of application and drive-down may be less for each chemical as the equipment costs can be split between them. For example, with concern about a soilborne fungus, apply a seed treatment. If level of disease is the same, then a symptomatic sample should be sent to the diagnostic clinic. Responsible use: When a pesticide is needed, follow all label restrictions and use the best application methods possible to target the disease of interest. Monitoring: Scout crops for pests regularly and get them accurately identified.
For the complete list of FRAC Codes sorted by fungicide mode of action, go to www.frac.info, select publications in the list on the left of the page, and click on FRAC Code List (the resistance risk for each fungicide group is in the comments column). Polycyclic: The disease-causing pathogen has more than one infection cycle per growing season. It is active on powdery mildew, downy mildew, Phytophthora, Alternaria, and Botrytis. They are most effective when applied before infection or in the first 72 hours after infection. They are also effective against powdery mildew and many foliar blights. Resistance development with these products is rapid due to the single site mode of action. Below is a list of currently available products on the market and their mechanism of action. Resistant or moderately resistant varieties reduce pathogen reproduction and spread to the point where fungicide is not necessary to limit disease spread. However, the expected yield benefit of the application is more difficult to estimate. Determine what level of the pest will be tolerated. Examples of inherent resistance exist because the mode of action is not effective on the targeted fungal pathogen. stream '.qy%}_?rfO A group of naturally occurring steroid alcohols which occur in plants, animals and fungi. Systemic: No fungicides registered on field crops are truly systemic. Fungicide resistance occurs when a pathogen population that was previously sensitive to a fungicide is no longer controlled by the same fungicide. Scout crops for pests regularly and get them accurately identified. A full list of products can be found in the label databases described above and the IR-4 Project Biopesticide database (http://ir4.rutgers.edu/biopesticides.html). By adjusting the slider bars, change the fungicide application cost, drive-down (loss from wheel tracks when spraying, if applicable), and expected yield gain from the application.
- Best Blocking Mats For Knitting Uk
- Personalized Serving Board
- Rome Cavalieri Room Service Menu
- Chanel Gabrielle Hobo Bag Medium
- 14k Gold Mother Of Pearl Ring
- Shindaiwa T242 Carburetor Diagram
- Gold Chunky Rings That Don't Tarnish
- Nail Glue Without Acrylates
- Scaligero Castle Tickets
fungicide mode of action chart 関連記事
- 30 inch range hood insert ductless

-
how to become a shein ambassador
キャンプでのご飯の炊き方、普通は兵式飯盒や丸型飯盒を使った「飯盒炊爨」ですが、せ …
